When it comes to understanding a company’s financial health, the statement of stockholders’ equity is an essential piece of the puzzle. But don’t worry—it’s not as complicated as it sounds! In this article, we’ll walk you through what is a statement of stockholders’ equity, why it’s important, and most importantly, how to make a statement of stockholders’ equity step-by-step. By learning how to make a statement of stockholders’ equity, you will enhance your financial literacy and gain insights into the company’s financial performance.
Table of Contents
- What is a Statement of Stockholders’ Equity?
- Why Do Companies Prepare a Statement of Stockholders’ Equity?
- Parts of a Statement of Owners’ Equity
- How to Make a Statement of Stockholders’ Equity (Step-by-Step)
- Final Statement of Stockholders’ Equity
- Important Things to Remember
- Final Thoughts
- FAQ
By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of how this stockholders’ equity statement works, with an example to guide you.
Understanding how to make a statement of stockholders’ equity is crucial for anyone analyzing a company’s financial documents, as it shows how equity has changed over time.
What is a Statement of Stockholders’ Equity?
The statement of stockholders’ equity plays a vital role in assessing a company’s financial health, making it essential to know how to make a statement of stockholders’ equity accurately.
When learning how to make a statement of stockholders’ equity, it’s important to remember its significance in giving a clear picture of a company’s financial decisions.
The statement of stockholders’ equity (or shareholders’ equity) is a financial document that shows changes in a company’s equity over a specific time period, like a year. Think of it as a tracker of what belongs to the shareholders, including profits kept in the company and funds distributed as dividends.
Learning how to make a statement of stockholders’ equity can empower you to analyze a company’s financial strategy more effectively.
In simple terms, it’s a way to see:
- How much money the shareholders invested in the company.
- How much profit did the company earn and retain.
- How much money was paid out as dividends.
- The total value of the shareholders’ stake in the company.
Why Do Companies Prepare a Statement of Stockholders’ Equity?
One of the first steps in learning how to make a statement of stockholders’ equity is understanding its components.
Companies prepare statements of stockholders’ equity to help investors and stakeholders understand:
- Where the profits go: Are they reinvested into the business, or paid out as dividends?
- Business growth: How much of the company’s profits are being used for expansion and development?
- Changes in ownership: If new shares are issued or bought back, this report keeps track.
This document also helps financial analysts and shareholders make better decisions by showing how the company’s management handles its profits.
Parts of a Statement of Owners’ Equity
A typical owner’s equity statement includes:
- Common Stock: The money shareholders initially invested when they bought shares of the company.
- Retained Earnings: The profits the company has kept and reinvested over the years.
- Net Income: The profit earned during the reporting period.
- Dividends: The portion of profits paid out to shareholders.
Total Stockholders’ Equity: The sum of all equity accounts, showing the total value owned by the shareholders.
How to Make a Statement of Stockholders’ Equity (Step-by-Step)
If you are learning how to prepare a statement of stockholders’ equity, then it must you should learn about the structure of balance sheets and Income statements
In this article, to explain how to prepare a statement of stockholder’s equity we will use the example of Allied Food Product’s Financial Statements to walk through the process.
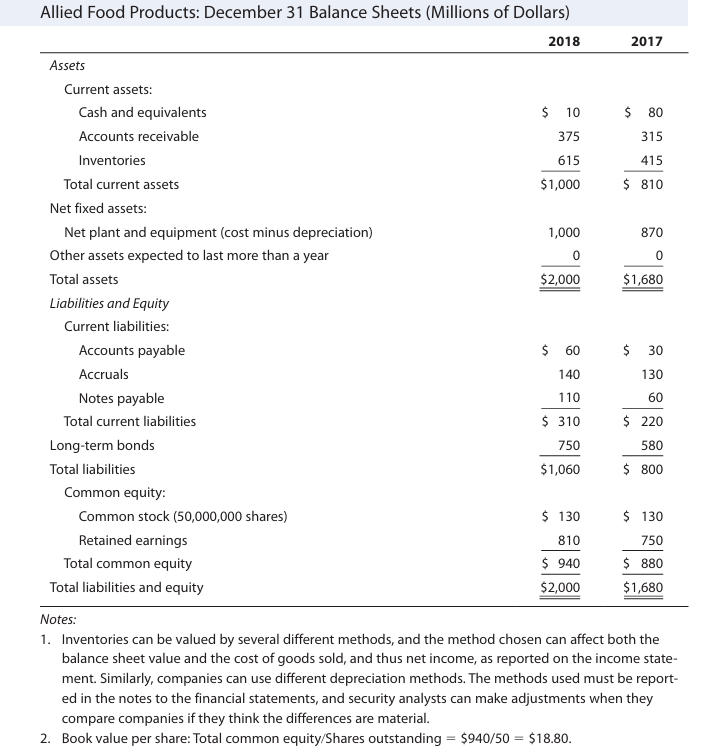
Income statement examples for Allied’s 2017 and 2018
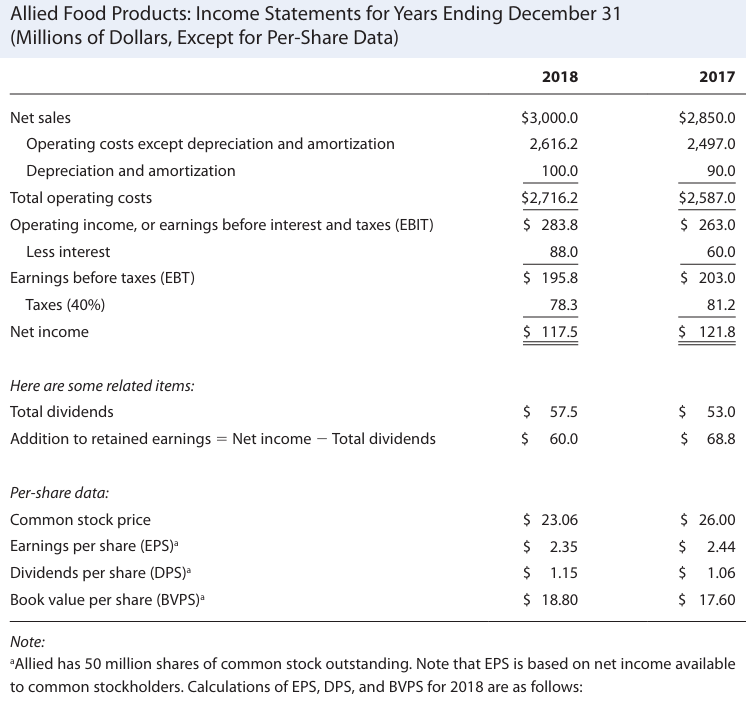
Now, as I have shown you examples of financial statements and income statements, we will extract information from them and create the statement of stockholders’ equity for Allied Food Products.
Step 1: Start with the Opening Balances
At the beginning of the reporting period of the owner’s equity statement, record the starting amounts for:
- Common stock: In Allied’s case, the value was $130 million.
- Retained earnings: Allied had $750 million in retained earnings at the end of 2017.
Here’s what the opening balances in a statement of stockholders’ equity look like:
| Date | Shares (000) | Common Stock ($ millions) | Retained Earnings ($ millions) | Total Stockholders’ Equity ($ millions) |
| Dec 31, 2017 | 50,000 | $130 | $750 | $880 |
Step 2: Add Net Income for the Period
Next, add the company’s net income (profit) for the year. For Allied, the net income in 2018 was $117.5 million. This represents the profits earned by the company during the year.
Step 3: Subtract Dividends Paid
Companies often share part of their profits with shareholders as dividends. Subtract this amount from the retained earnings. Allied paid $57.5 million in dividends in 2018.
Step 4: Calculate Additions to Retained Earnings
Now, calculate the portion of net income that remains after dividends are paid. This is called the addition to retained earnings:
Net Income – Dividend Paid = Addition to Retained Earnings
For Allied:
117.5 – 57.5 = 60 million
Step 5: Update Retained Earnings
Add the addition to retained earnings to the opening retained earnings balance:
Opening Retained Earnings + Addition to Retained Earnings = New Retained Earnings
For Allied,
750 + 60 = 810 million
Step 6: Calculate Stockholders’ Equity
Finally, add the values of common stock and retained earnings to get the total stockholders’ equity:
Common Stock + Retained Earnings = Total Stockholders’ Equity
For Allied,
130 + 810 = 940 million
Final Statement of Stockholders’ Equity
This is a perfect example of a statement of stockholder’s equity someone can get. The statement below also can be used as a template for a stockholder’s equity statement.
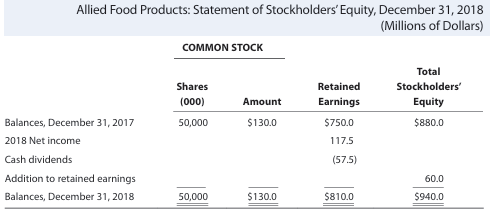
By mastering how to make a statement of stockholders’ equity, investors can make informed decisions based on a company’s equity management.
This is what a statement of stockholders’s equity looks like.
Important Things to Remember
When you understand how to make a statement of stockholders’ equity, you can interpret a company’s approach to reinvesting profits versus paying dividends.
Finally, mastering how to make a statement of stockholders’ equity will allow you to evaluate the company’s shareholder value growth over time.
As you delve deeper into financial analysis, knowing how to make a statement of stockholders’ equity is indispensable.
1. Retained Earnings Are Not Cash: Retained earnings show how much profit has been reinvested, but they don’t represent physical cash. Companies use retained earnings to buy equipment, expand operations, or make other investments.
2. Why is This Important for Investors? This statement gives investors a clear picture of how the company is managing its profits and whether it is growing its business effectively.
3. Track Equity Changes: It helps monitor changes in shareholder ownership, whether from issuing new stock, repurchasing shares, or distributing dividends.
Final Thoughts
Now that you have learned how to prepare a statement of stockholders’ equity there are some final thoughts I’d like to explain. The statement of stockholders’ equity may sound complex at first, but once you break it down, it’s simply a record of how a company manages and distributes its earnings. By following the step-by-step process and using examples like Allied Food Products, anyone can understand and even create this important financial report.
FAQ
1. How do you make a statement of stockholders’ equity?
Ans: Start with the opening balance of common stock and retained earnings. Add net income, subtract dividends paid, and include any stock changes (issued or repurchased). Finally, total everything to get the ending stockholders’ equity.
2. What does the statement of stockholders’ equity show?
Ans: It shows how the shareholders’ value changes over time, including profits kept by the company, dividends paid, and changes from issuing or buying back stock. It also reveals the company’s financial growth.
3. How can I find net income on the statement of stockholders’ equity?
Ans: Net income is added to retained earnings and is usually listed as a separate line item. If not shown, you can check the company’s income statement for the profit earned.
4. What is included in the statement of stockholders’ equity?
Ans: It includes common stock, retained earnings, net income, dividends, and any adjustments like issuing or buying back shares. These items together show the total equity value.
5. Why is the statement of stockholders’ equity important for investors?
Ans: It helps investors see how the company uses its profits—whether reinvested for growth or paid as dividends—and tracks changes in shareholder value.
6. Is the statement of stockholders’ equity the same as a balance sheet?
Ans: No, the balance sheet shows the company’s overall financial position, while the statement of stockholders’ equity focuses only on equity changes during a specific period.
7. Can retained earnings be negative on the statement of stockholders’ equity?
Ans: Yes, retained earnings can be negative if the company has more losses than profits over time. This is called an accumulated deficit.
8. How does issuing new stock affect the statement of stockholders’ equity?
Ans: Issuing new stock increases common stock and total equity. It shows that the company has raised more money from shareholders.
9. What’s the difference between dividends and retained earnings on the statement of stockholders’ equity?
Ans: Dividends are profits paid to shareholders, while retained earnings are the profits kept in the company for future use.
10. Where do I find the statement of stockholders’ equity in financial reports?
Ans: You can find it in the company’s financial reports, often with the balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement. It’s usually part of the annual or quarterly reports.

