In this blog, I have described the process of determining the degree of financial leverage. However, before that, we need to be aware of the theoretical aspects to understand the entire process. The theoretical component can also be understood, allowing us to interpret the findings in the future when calculating the degree of financial leverage (DFL).
Table of Contents
- What is called the Degree of Financial Leverage (DFL)?
- What are the differences between the financial leverage and the degree of financial leverage?
- Why should we compute the degree of financial leverage (DFL)?
- Calculating the degree of financial leverage
- Final Thoughts
What is called the Degree of Financial Leverage (DFL)?
A Degree of Financial Leverage (DFL) is a financial ratio, which indicates the sensitivity of Earnings Per Share (EPS) of a company to changes in the operating profit (EBIT) of the company. Basically, it demonstrates the extent to which the EPS will vary with each 1% variation in EBIT.
What are the differences between the financial leverage and the degree of financial leverage?
Financial leverage measures the use of debt in financing on the other hand DFL evaluates how sensitive a company’s net income or earnings per share (EPS) is to changes in operating income (EBIT). Understanding both concepts is crucial for assessing financial risk and making informed investment and financing decisions. The basic differences include:
- Definition: Financial leverage measures the amount of debt used in a company’s capital structure, whereas DFL is the impact of change in EBIT on net income or EPS.
- Purpose: Financial leverage is considered to be the use of debt to finance a company and DFL is used to measure the sensitivity of earnings to financial leverage.
- Formula: Financial leverage uses total debt and equity, whereas DFL uses EBIT and interest expenses.
- Risk Measurement: Financial leverage assesses overall debt risk; DFL shows how much profits can fluctuate due to leverage.
- Scope: Financial leverage is a static measure of capital structure; DFL is dynamic, which means that it reflects how income is responsive to profits.
- Impact: Large financial leverage implies a higher amount of debt and large DFL implies that a slight change in income can lead to a significant change in profits.
Why should we compute the degree of financial leverage (DFL)?
- Measure Financial Risk: This is used to measure the risk of debt utilization in the capital structure of the company.
- Understand Earnings Volatility: Refers to the extent to which EPS is going to vary with the variation of operating income (EBIT), indicating the stability of earnings.
- Evaluate Debt Impact: Determine the effect of current debt on shareholder returns and profitability.
- Support Decision-Making: Assists the management in making sound financing and investment decisions depending on the risk they take.
- Investor Insight: This gives investors a clue of the possible variations in returns that help them in assessing the financial status of the business.
Calculating the degree of financial leverage
The degree of financial leverage formula

This means that DFL shows the ratio of the percentage change in EPS to the percentage change in EBIT. A higher DFL indicates that the company is using more financial leverage, which means it is more dependent on debt.
There are two alternative ways to calculate the degree of financial leverage.
Alternative 1
The Degree of Financial Leverage Formula at the EBIT level:
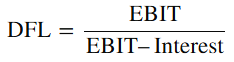
Let’s break down what each term means:
- EBIT: Earnings Before Interest and Taxes. This is the company’s operating income before paying interest on debt.
- Interest (I): The fixed interest expenses that the company must pay on its debt.
- Step-by-Step Explanation:
1. Calculate EBIT: Find the company’s operating income (revenue minus operating expenses). This is the starting point, as it represents the company’s earnings from its core operations before any interest or taxes are considered.
2. Subtract Interest Expenses: Deduct the fixed interest expenses from EBIT. This tells you the earnings left after paying interest on the company’s debt.
3. Apply the Formula: Divide the original EBIT by the result obtained in Step 2 (EBIT – Interest). This ratio tells you how much the EPS will change for every 1% change in EBIT.

4. Interpret the Result: The higher the DFL, the more sensitive the company’s EPS is to changes in EBIT. This means that if the DFL is high, a small percentage change in EBIT will cause a larger percentage change in EPS.
Let’s understand the formula with an example:
Let’s say Company A has the following information:
- EBIT = $100,000
- Interest Expense = $20,000
Now, let’s calculate the DFL:
- Subtract Interest from EBIT:
EBIT−Interest=100,000−20,000
=80,000
Calculate the degree of financial leverage (DFL)
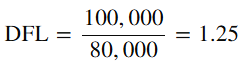
Interpret the result:
A DFL of 1.25 means that for every 1% change in EBIT, the EPS will change by 1.25% that amount. If EBIT increases by 10%, the EPS will increase by 12.5% (10% x 1.25).
Alternative 2
The degree of financial leverage formula at the quantity level
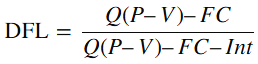
Formula Explanation:
- Q: Quantity of units sold or produced.
- P: Price per unit.
- V: Variable cost per unit.
- FC: Fixed Costs.
- Int: Interest expenses.
Breaking down the formula:
- 1. Calculate Contribution Margin:
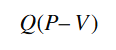
Subtract the total variable costs from total sales revenue to get the contribution margin. The contribution margin shows how much is left after covering variable costs, which can then be used to cover fixed costs and generate profit
2. Calculate Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT):
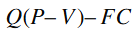
Subtract fixed costs (FC) from the contribution margin. This gives you the EBIT, which is the profit before paying interest on debt and taxes.
3. Calculate Profit After Paying Interest:
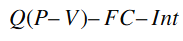
Subtract interest expenses (Int) from EBIT. This tells you the profit left after paying interest on debt, which goes to the shareholders.
Let’s understand this DFL formula with an example:
Assumptions:
- Quantity of units sold (Q) = 500 units
- Price per unit (P) = $50
- Variable cost per unit (V) = $30
- Fixed Costs (FC) = $5,000
- Interest expense (Int) = $2,000
Calculate DFL:
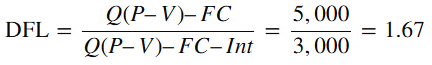
This DFL value of 1.67 means that if EBIT changes by 1%, EPS will change by 1.67%. In other words, using debt has increased the sensitivity of earnings for shareholders.
Final Thoughts
To sum up, the Degree of Financial Leverage (DFL) is a very important financial indicator that assists in determining the sensitivity of the Earnings Per Share (EPS) of a company to the variations in its operating income (EBIT). Through the knowledge of the DFL, companies and investors are able to determine the possible effects of debt on profitability, earnings volatility, and financial risk. A high DFL implies that EPS is more sensitive to EBIT changes, which can increase profits and losses. Both EBIT and quantity-level formula of calculating DFL are useful in the determination of financial leverage and risk exposure of the company, which is instrumental in making informed decisions by both management and investors.


